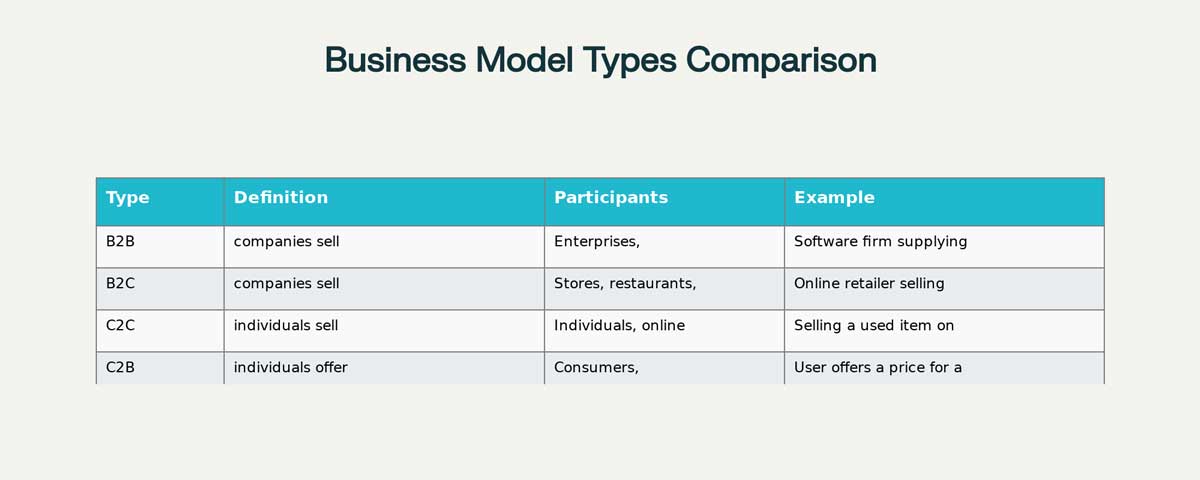
B2B, C2C, G2G… cunning abbreviations, simple definitions

B2B, B2C, C2C, C2B and other types of business. Source: shutterstock.com
In the age of e-commerce, we constantly face new crafty words and abbreviations. However, most of them look terrifying at first sight only. In fact, the vast majority of these words are simple and logical.
B2B
B2B (Business-To-Business) is a commercial activity (business) between two companies. So the clients of one enterprise are other companies. The use of internet technologies in the commercial communication of enterprises creates new business connections, speeds up transactions, facilitates the process of purchasing and selling goods, materials, equipment, and products.
The sizes of companies, engaged in B2B, can be different – from the smallest to the largest. Let’s say, very small barbershops can be consumers of products of large (mass-production) factories, which produce hair clippers, trimmers, and other similar equipment. And vice versa: a small firm, consisting of ten developers, can supply entire corporations with exclusive software.
Originally, the term was used to describe any type of process of selling products between enterprises. Today, it is more commonly used to describe online transactions between companies.
The most popular B2B types:
- Engineering and machinery (auto industry, airplane industry, shipbuilding, etc). But you should remember that when, for instance, Mercedes Benz produces its vehicles and sells them to end users (individuals), it is B2C. However, the plant doesn’t sell cars directly to people. Usually, such enterprises implement this through an authorized dealer network, thus it is B2B. Authorized dealers, in turn, will sell cars to individuals, which makes it a B2C situation. But if an authorized dealer sold vehicles to a transport company, it again will become a B2B case;
- Commodity and metal processing companies. When an enterprise that does the job of exploiting oil, sells it to oil-processing plants it is B2B. Oil refineries sell it to gas stations, and they are B2B companies for the latter. Finally, when you get some gas from a gas station, it is definitely a B2C case;
- Chemical industry;
- Wood processing;
- Advertising and marketing services. Mostly, individuals don’t need marketing and advertising. Thus, this industry is a B2B representative.
There are many other examples of industries, but they depend on the country, economy, and many other factors.
B2C
B2C (Business-To-Consumer) is a commercial activity between companies and consumers. It can be a huge supermarket, online store, or even a small branch of a law firm (consulting individuals).
Initially, the term was used to define any type of process of selling products directly to consumers, including shopping in-store or eating in a restaurant. Nowadays, it is used to describe transactions between online retailers and their customers.
The most popular B2C types:
- Stationary points of sale. It is about all kinds of brick-and-mortar stores. Any large or small shop near your house, even a tobacco kiosk, is a B2C business;
- Mobile points of sale. Hot dogs on wheels, portable coffee carts, and even individuals (entrepreneurs) that sell goods on the street are good examples of mobile points of sale;
- Catering, such as fast food networks (McDonald’s or Burger King), cafes, restaurants, diners, bars, pubs, etc.;
- E-commerce. It is the biggest sector, including all kinds of online stores, from specialized (for example, Oriflame or DeWalt) to general (like Amazon) ones. It is about any product or service aimed at the final consumer.
C2C
C2C (Consumer-To-Consumer) is a commercial activity between private individuals (consumers). This business model can be implemented directly, as well as through a third-party (mediator).
Initially, the C2C model implies direct sales between individuals. Today, it is more about online sales between individuals. In this case, a need for a third-party emerges (marketplaces and classified advertisements sites, such as eBay, Craigslist, or Gumtree). Thus, if you buy an iPad on eBay from an individual, not an entrepreneur, it is a classic C2C model. If you sell a chainsaw to your neighbor, it is also an example of C2C, however, an offline “old-school” type.
C2B
C2B (Consumer-To-Business) is a little unusual model of e-commerce. Consumers define (bid) prices on goods and services (offered by businesses) by themselves. An American company Priceline.com is a typical example of C2B. Thus, the company is more like a broker, which searches for firms that are ready to sell goods or services for the bid (by the customer) prices.
E-Government
E-government is the use of electronic communications devices (computers, Internet, etc) to provide public services in a country or region.
With the modern development of technology, it is quite logical to move some interaction with the government and state to the electronic form. It includes the collection of taxes and duties, registration of vehicles and small and medium-sized businesses, communication with the traffic police, etc.
Thus, there are new abbreviations and definitions:
- G2G (Government-To-Government) is commerce between government authorities and institutions.
- B2G (Business-To-Government) is a commercial activity between companies and the public sector. Public tenders, businesses that pay taxes, file reports, selling goods to governmental institutions are the best examples of B2G model.
- G2C (Government-To-Citizens) is relationships between organizations (subjects) of public administration and citizens.
SEE ALSO:
- M-commerce: all you need to know about it
- What is VAT and how does it work?
- Throwback Thursday: the complete guide to POS
In the high-tech sector, B2B relationships are fundamental for advancing technological solutions and innovations. Tech providers like IBM and Oracle serve as backbone systems for other businesses, offering everything from cloud services to artificial intelligence solutions. The collaboration amongst B2B companies in tech results in richer data integration, improved security protocols, and a faster pace of digital transformation within various industries.
B2B markets are also seeing an increase in subscription-based and as-a-service models, particularly in software (SaaS), platform (PaaS), and infrastructure (IaaS). These models offer scalability and flexibility, which are highly valued by businesses looking to maintain competitiveness in a rapidly changing technological environment.
The healthcare sector benefits significantly from B2B arrangements, where pharmaceutical companies provide hospitals with critical drugs and medical devices. These partnerships often extend into collaborative research for drug development, showcasing a complex web of inter-company collaborations that go beyond mere supply chains.
Additionally, B2B digital platforms are leveraging AI to facilitate smarter and more dynamic matchmaking between businesses. These platforms use algorithms to analyze business needs, market trends, and potential partnership synergies, thus streamlining the B2B process and increasing efficiency.
On the B2C front, businesses are increasingly adopting a direct-to-consumer (DTC) model, bypassing traditional retailers and intermediaries. Brands like Nike and Casper are engaging consumers directly through their websites and specialized stores. This shift not only helps businesses to gather rich consumer data but also allows them to control their brand narrative and consumer experience more tightly.
In terms of customization, B2C companies are using technology to offer personalized experiences and products. From personalized marketing messages based on consumer behavior to custom-built products, personalization is becoming a significant trend in B2C, driven by consumer demand for products that align more closely with personal preferences and needs.









